Overview
In this topic, we are going to discuss the social differentiation of the indian society, in which we will discuss various categories of social differentiation; varnashrama dharma, varna, jati, gotra, pravara, family, slavery, and untouchability in Hindu society. Let us understand all these terms in brief. But firstly let us know about the term Varnashrama dharma. It refers to the two key concepts of varna and ashram, in which varna refers to the color or class, and ashram refers to the process of guiding an individual through the various phases of learning. So let us understand other key concepts of social differentiation in brief.
Social differentiation
VARNA
The term varna refers to the division of the entire society into four main classes in Hindu tradition which are as follows
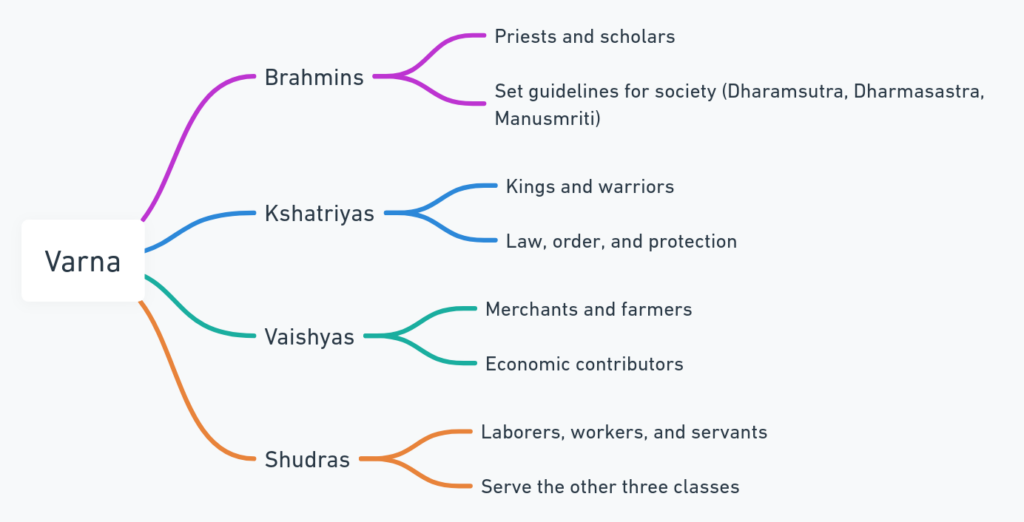
- Brahmins
This group of people generally refers to those who did prayers in the temple called priests and scholars who set guidelines to the entire society by their text, like dharamasutra, dharmasastra, and manusmriti.
- Kshatriyas
These groups of people include kings and warriors who make law and order for their subjects and provide protection to them. They have control power and other administrative authority.
- Vaishyas
This group of people includes the merchants and farmers who serve both by their money and products.
- Shudras
These groups of people are very low in the entire group of society, they provide their services to all three classes as laborers workers, and servants.
JATI
The term jati refers to the subgroups of entire social classes which is based on their occupation. As time passes all these jatis make their association within the society with status and lineage.

GOTRA
Gotra refers to the lineage of a person which commonly comes from ancestors, In the gotra system the woman did not inherit the same gotra of her family, she adopted his husband’s gotra, while the son inherited the father’s gotra. There is a rule in the gotra system that the same gotra people can not marry each other because they are siblings due to the same gotra.

PRAVARA
The term bravura refers to the ritualist recitation of one ancestor’s name during the ceremonies. It has been established by one in the family of lineage and it identifies as the specific gotra of a particular family.

FAMILY
Family plays a significant role in the society of Hinduism, which serves the entire society as a basic unit of social organization. The structure of the family often extends beyond the nuclear family which includes relatives to extend it.

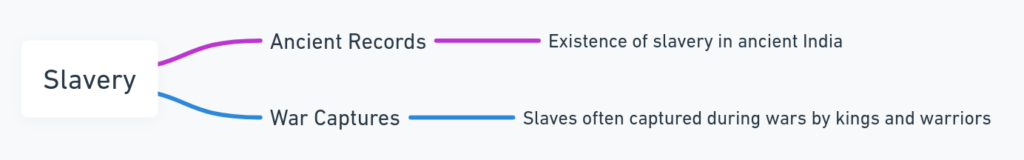
SLAVERY
The varnashrama dharma does not inherit this term slave, it has been noted in the ancient record that there was a slavery rule in ancient India. The slaves were often get captured in the wars by many kings, or warriors.
UNTOUCHABILITY
Untouchability was established in ancient India by our ancestors. The term untouchability is associated with the social practices in which some caste people were regarded as impure, and relegated to menial tasks. They often face various kinds of discrimination, and inequality, segregation through others. It is now abolished in India but still, we see the same in some societies.

CONCLUSION
All these concepts have been collected and shaped the social structure in Hindu society by various traditional factors. It has been influenced by various aspects of social life, occupation, marriage, and social interaction, etc. although from all these significant things we can note here how the practice, and interpretation of ancient times have evolved with time, and in the modern era we are subjected for the same., and now our modern Hindu society is diverse and complex.
